[ Instrument Network Instrument R & D ] Recently, Li Can and Li Rengui's team at the State Key Laboratory of Catalysis, Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences have made new progress in the research of the essential role of exposed crystal planes of semiconductor photocatalysts. The surface-dependent relationship confirms that the difference in photocatalytic activity of the active crystal plane is determined by the photogenerated charge separation properties between the different coexisting exposed crystal planes.
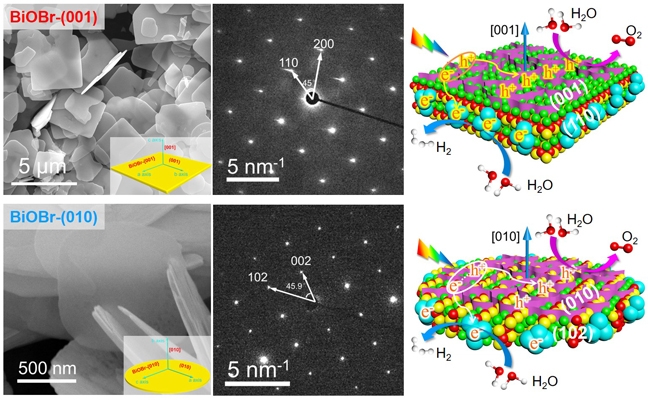
The artificial photo-synthesis of solar fuel is a "holy grail" scientific subject in the international scientific field, and the separation of photogenerated charges is the core scientific issue of artificial photo-synthesis. Li Can's team has long been committed to the research of artificial photo-synthetic solar fuel, and has made a series of progress: He has proposed a heterogeneous junction charge separation mechanism (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2008; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2012) Photogenerated charge separation effect between crystal planes (Nature Commun. 2013; Energy Environ. Sci. 2014), developed a photosymmetric charge separation strategy for highly symmetrical semiconductor materials (Energy Environ. Sci. 2016), and proposed polarity-induced photogenerated charge separation New strategy (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2020), and independently developed a new technology for photogenerated charge imaging characterization (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2015; Nature Energy, 2018) and so on. In particular, the strategy of photogenerated charge separation between crystal planes proposed by the team in recent years has developed into one of the most concerned research directions in the field of solar photocatalysis.
Although the morphology and crystal plane control of semiconductor photocatalytic materials have proven to be one of the effective ways to improve the photocatalytic performance, there are still divergent opinions on how the morphology and crystal plane affect the photocatalytic performance, and researchers often attribute the differences in photocatalytic activity The so-called highly active crystal plane, but the understanding of the nature of the active crystal plane is not clear. In this work, the research team based on the previous research on the separation of photogenerated charges between crystal planes, using a typical bismuth oxybromide (BiOBr) semiconductor as a research model, two kinds of BiOBr nanocrystals with specific crystal planes were controllably synthesized. The study found that the difference in photocatalytic activity of nanocrystals with specific crystal planes exposed is not directly related to the properties of the crystal planes with a high exposure ratio, but is closely related to the properties of the crystal planes that are co-exposed to them. These coexisting crystal planes Although the exposure ratio is small, its existence really determines the properties of the high exposure ratio crystal plane in the photocatalytic reaction. The difference in surface band curvature between low-exposure and high-exposure crystal planes induces spatial separation of photogenerated charges between different crystal planes, and the difference in photogenerated charge separation properties between crystal planes due to different coexisting crystal planes. , Directly affects the nanocrystals show different catalytic performance in photocatalytic reactions. This research work further clarifies the nature of photocatalytic reactions that depend on the crystal plane of semiconductor photocatalysts, and has important scientific value for deep understanding of the photogenerated charge separation and catalytic reaction mechanism of semiconductor nanophotocatalysts.
The research results were published in Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., With the first author Shi Ming, a doctoral student. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Chinese Academy of Sciences Strategic Leading Science and Technology Special Project A "Transformative Clean Energy Key Technologies and Demonstrations" sub-projects, and the Xingliao Talent Program.
"Gravity Die Casting. A permanent mould casting process, where the molten metal is poured from a vessle of ladle into the mould, and cavity fills with no force other than gravity, in a similar manner to the production of sand castings, although filling cn be controlled by tilting the die."
Gravity Die Casting
Sometimes referred to as Permanent Mould, GDC is a repeatable casting process used for non-ferrous alloy parts, typically aluminium, Zinc and Copper Base alloys.
The process differs from HPDC in that Gravity- rather than high pressure- is used to fill the mould with the liquid alloy.
GDC is suited to medium to high volumes products and typically parts are of a heavier sections than HPDC, but thinner sections than sand casting.
There are three key stages in the process.
-
The heated mould [Die or Tool] is coated with a die release agent. The release agent spray also has a secondary function in that it aids cooling of the mould face after the previous part has been removed from the die.
-
Molten metal is poured into channels in the tool to allow the material to fill all the extremities of the mould cavity. The metal is either hand poured using steel ladles or dosed using mechanical methods. Typically, there is a mould [down sprue" that allows the alloy to enter the mould cavity from the lower part of the die, reducing the formation of turbulence and subsequent porosity and inclusions in the finished part.
-
Once the part has cooled sufficiently, the die is opened, either manually or utilising mechanical methods.
Advantages
-
Good dimensional accuracy
-
Smoother cast surface finish than sand casting
-
Improved mechanical properties compared to sand casting
-
Thinner walls can be cast compared to sand casting
-
Reverse draft internal pockets and forms can be cast in using preformed sand core inserts
-
Steel pins and inserts can be cast in to the part
-
Faster production times compared to other processes.
-
Once the tolling is proven, the product quality is very repeatable.
-
Outsourced Tooling setup costs can be lower than sand casting.
Gravity Casting Parts
Gravity Casting Parts,Aluminum Alloy Gravity Casting Parts,Aluminum Gravity Die Casting Parts,Gravity Casting Aluminum Parts
HSI INDUSTRIEL LTD , https://www.hsiindustriel.com
